
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
- Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):643-652. Published online August 7, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0041
- 2,264 View
- 207 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
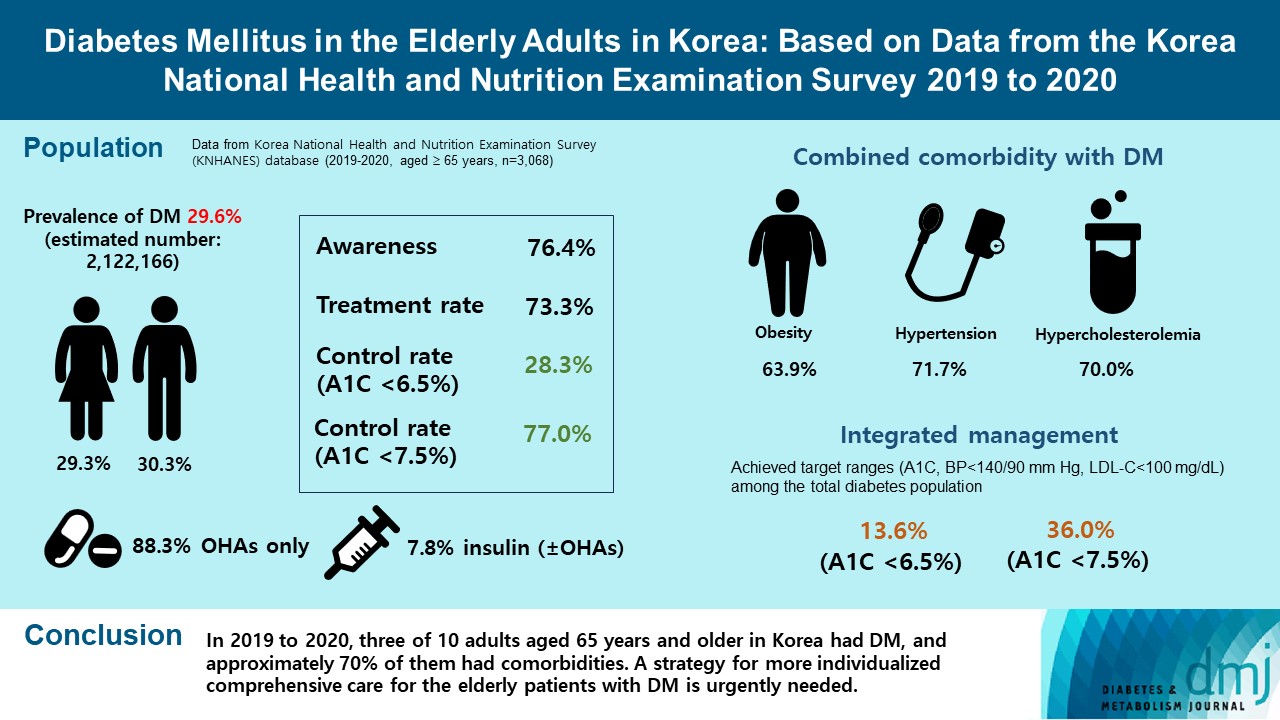
We evaluated the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus (DM) in elderly Korean patients based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES).
Methods
A total of 3,068 adults aged 65 years and older (19.8% of total population) were analyzed using KNHANES from 2019 to 2020. Prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates, and comorbidities were analyzed. Lifestyle behaviors and energy intake were also measured.
Results
The prevalence of DM and prediabetes was 29.6% and 50.5%, respectively. The awareness, treatment and control rates were 76.4%, 73.3%, and 28.3%, respectively. The control rate was 77.0% if A1C <7.5% criteria was used. The mean A1C value of individuals with known DM was 7.1%, and 14.5% of the known DM patients had A1C ≥8.0%. Abdominal obesity, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia were combined with DM in 63.9%, 71.7%, and 70.7%, respectively, and the rate of integrated management was 36.0% (A1C <7.5% criteria). A total of 40.1% of those with DM walked regularly. The percentage of energy intake from carbohydrates was higher in those with DM than in those without DM (P=0.044), while those of fat (P=0.003) and protein (P=0.025) were lower in those with DM than in those without DM in women.
Conclusion
In 2019 to 2020, three of 10 adults aged 65 years and older in Korea had DM, and approximately 70% of them had comorbidities. A strategy for more individualized comprehensive care for the elderly patients with DM is urgently needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association Between High Blood Folate Levels and Glaucoma in a Representative Korean Population
Ji Young Lee, Jin A. Choi, Sung Pyo Park, Donghyun Jee
Investigative Opthalmology & Visual Science.2024; 65(1): 6. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef
- Association Between High Blood Folate Levels and Glaucoma in a Representative Korean Population
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):201-210. Published online February 8, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0375
- 3,263 View
- 217 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
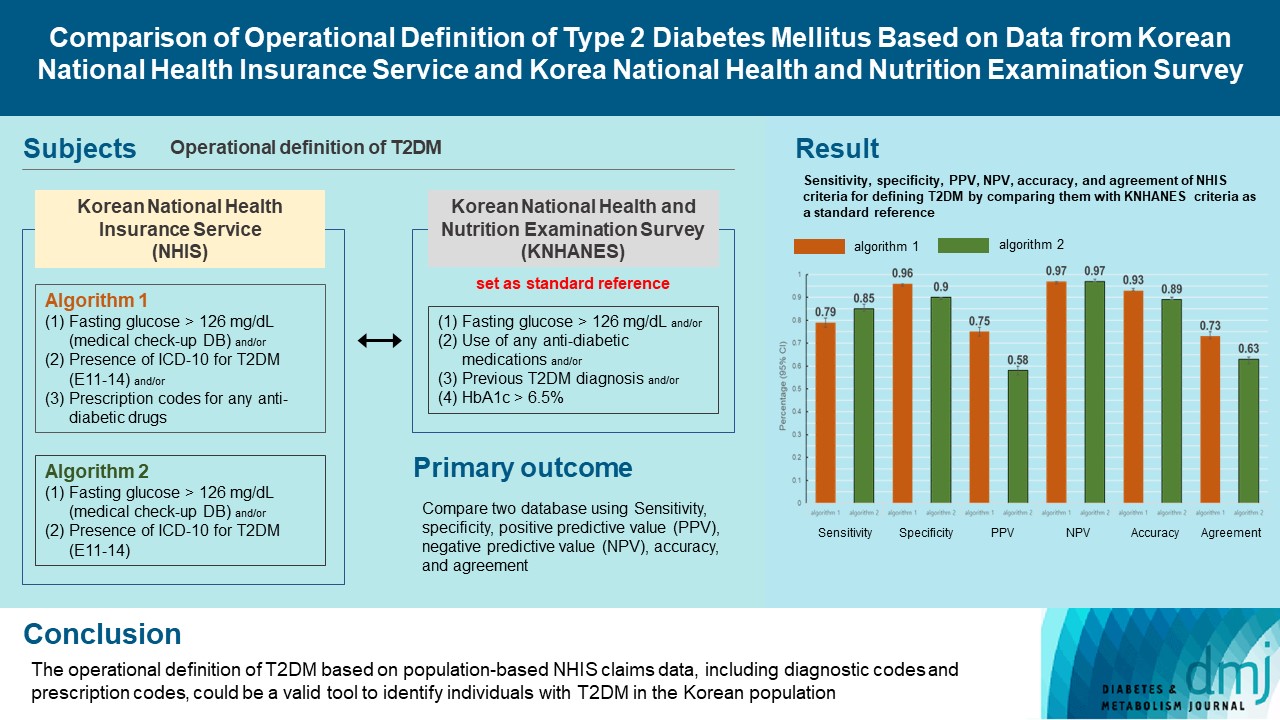
We evaluated the validity and reliability of the operational definition of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database.
Methods
Adult subjects (≥40 years old) included in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) from 2008 to 2017 were merged with those from the NHIS health check-up database, producing a cross-sectional dataset. We evaluated the sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, and agreement of the NHIS criteria for defining T2DM by comparing them with the KNHANES criteria as a standard reference.
Results
In the study population (n=13,006), two algorithms were devised to determine from the NHIS dataset whether the diagnostic claim codes for T2DM were accompanied by prescription codes for anti-diabetic drugs (algorithm 1) or not (algorithm 2). Using these algorithms, the prevalence of T2DM was 14.9% (n=1,942; algorithm 1) and 20.8% (n=2,707; algorithm 2). Good reliability in defining T2DM was observed for both algorithms (Kappa index, 0.73 [algorithm 1], 0.63 [algorithm 2]). However, the accuracy (0.93 vs. 0.89) and specificity (0.96 vs. 0.90) tended to be higher for algorithm 1 than for algorithm 2. The validity (accuracy, ranging from 0.91 to 0.95) and reliability (Kappa index, ranging from 0.68 to 0.78) of defining T2DM by NHIS criteria were independent of age, sex, socioeconomic status, and accompanied hypertension or dyslipidemia.
Conclusion
The operational definition of T2DM based on population-based NHIS claims data, including diagnostic codes and prescription codes, could be a valid tool to identify individuals with T2DM in the Korean population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in young Korean adults
Junchul Ha, Oak-Kee Hong, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; : 111584. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef
- Metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease increases the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in young Korean adults
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):578-591. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0135
- 5,903 View
- 230 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Estrogen promotes glucose homeostasis, enhances insulin sensitivity, and maintains counterregulatory responses in recurrent hypoglycemia in women of reproductive age. Postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) might be more vulnerable to severe hypoglycemia (SH) events. However, the relationship between reproductive factors and SH occurrence in T2DM remains unelucidated.
Methods
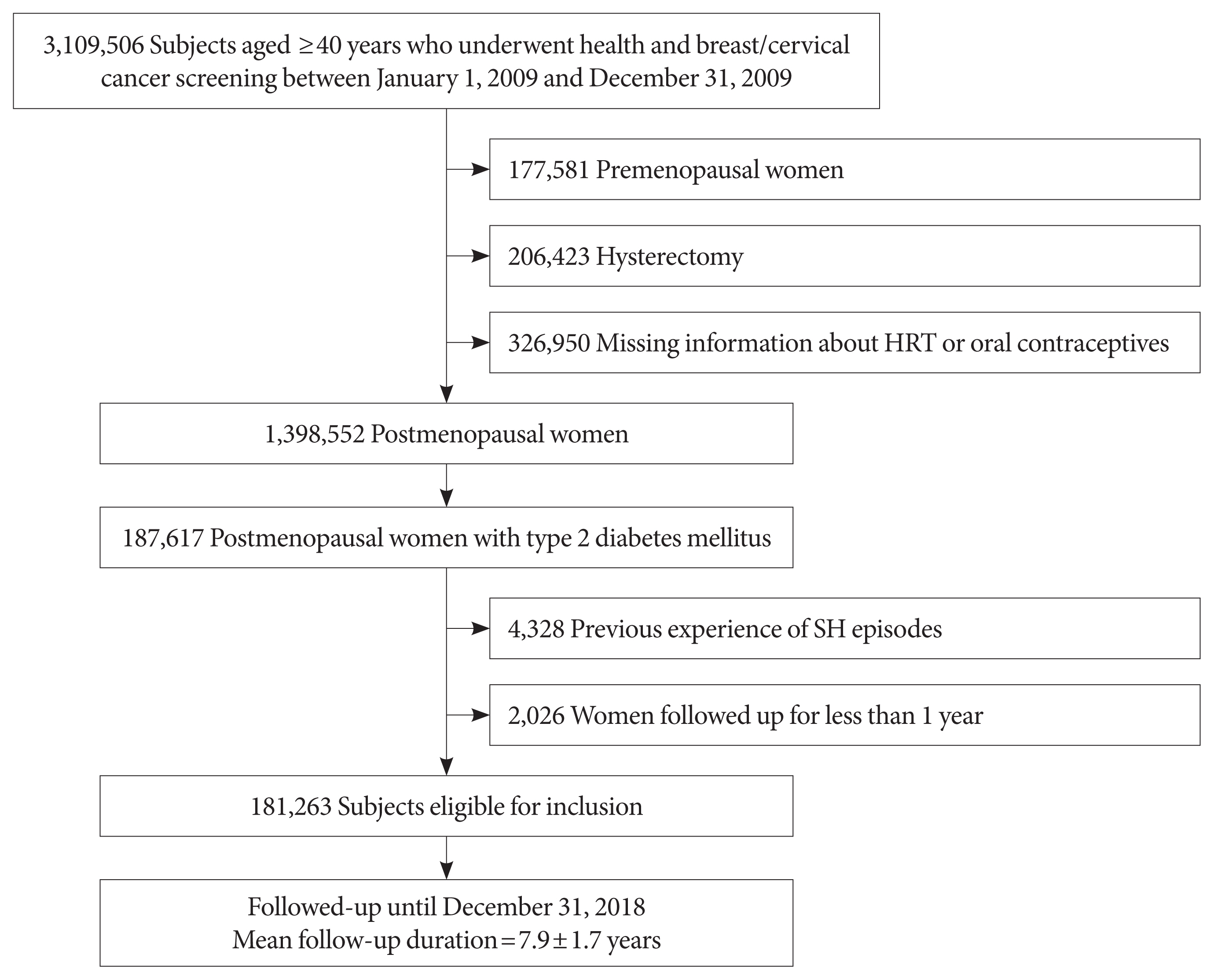
This study included data on 181,263 women with postmenopausal T2DM who participated in a national health screening program from January 1 to December 31, 2009, obtained using the Korean National Health Insurance System database. Outcome data were obtained until December 31, 2018. Associations between reproductive factors and SH incidence were assessed using Cox proportional hazards models.
Results
During the mean follow-up of 7.9 years, 11,279 (6.22%) postmenopausal women with T2DM experienced SH episodes. A longer reproductive life span (RLS) (≥40 years) was associated with a lower SH risk compared to a shorter RLS (<30 years) (adjusted hazard ratio [HR], 0.74; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.69 to 0.80; P for trend <0.001) after multivariable adjustment. SH risk decreased with every 5-year increment of RLS (with <30 years as a reference [adjusted HR, 0.91; 95% CI, 0.86 to 0.95; P=0.0001 for 30−34 years], [adjusted HR, 0.80; 95% CI, 0.76 to 0.84; P<0.001 for 35−39 years], [adjusted HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.68 to 0.81; P<0.001 for ≥40 years]). The use of hormone replacement therapy (HRT) was associated with a lower SH risk than HRT nonuse.
Conclusion
Extended exposure to endogenous ovarian hormone during lifetime may decrease the number of SH events in women with T2DM after menopause. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Yi Yuan, Tong-Yu Peng, Guang-Yuan Yu, Zhao Zou, Meng-Ze Wu, Ruofei Zhu, Shuang Wu, Zi Lv, Su-Xin Luo
International Journal of Environmental Health Research.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Reproductive Lifespan and Motor Progression of Parkinson’s Disease
Ruwei Ou, Qianqian Wei, Yanbing Hou, Lingyu Zhang, Kuncheng Liu, Junyu Lin, Tianmi Yang, Jing Yang, Zheng Jiang, Wei Song, Bei Cao, Huifang Shang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6163. CrossRef - Menopause and development of Alzheimer’s disease: Roles of neural glucose metabolism and Wnt signaling
Paulina Villaseca, Pedro Cisternas, Nibaldo C. Inestrosa
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between serum copper level and reproductive health of Women in the United States: a cross-sectional study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Importance of Awareness and Treatment for Diabetes in Influenza Vaccination Coverage of Diabetic Patients under 65 Years: A Population-Based Study
- Yu Mi Ko, Seung Hyun Ko, Kyoungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Joon Young Choi, Shin Young Kim, So Hyang Song, Chi Hong Kim, Sung Kyoung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):55-66. Published online May 29, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0189
- 6,969 View
- 138 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Influenza is a global public health problem causing considerable morbidity and mortality. Although vaccination is the most effective way to prevent infection, vaccination coverage is insufficient in people with chronic disease under 65 years, especially diabetes. The purpose of this study was to evaluate influenza vaccination coverage and identify factors associated with influenza vaccination in Korean diabetic adults under 65 years.
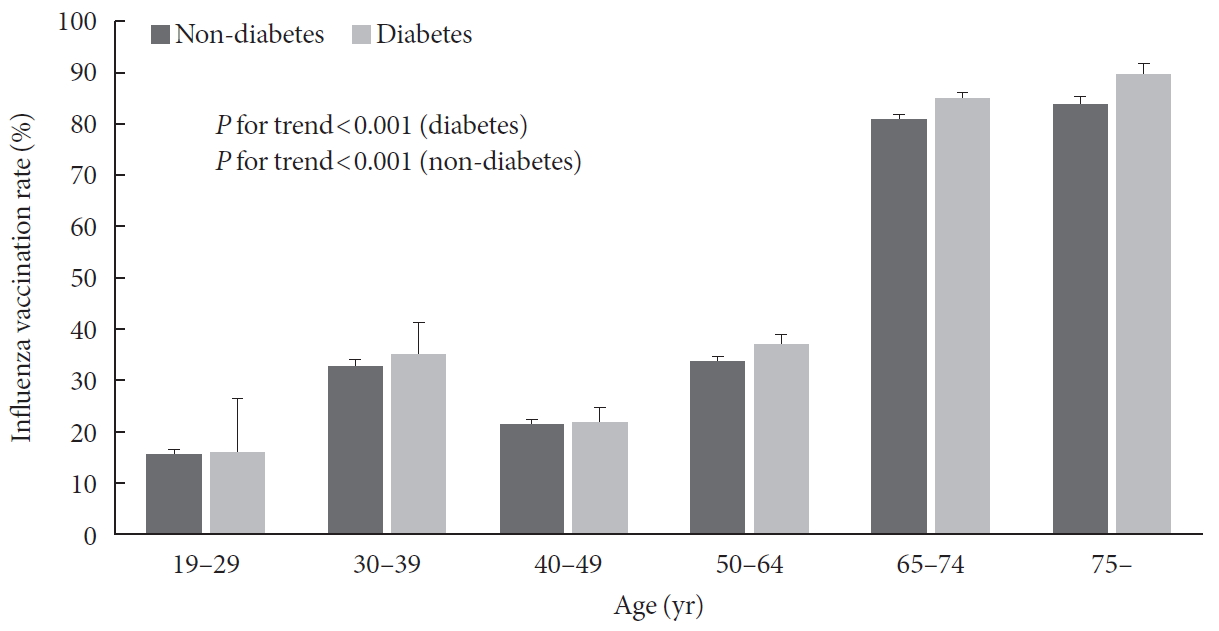
Methods Data were obtained from 24,821 subjects in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2014 to 2017). Socioeconomic, health-related, and diabetic factors were investigated for their relations with influenza vaccination in diabetic patients under 65 years using univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results Among 24,821 subjects, 1,185 were diabetic patients under 65 years and their influenza vaccination rate was 36.5%. Socioeconomic (older age, female gender, non-smoker, light alcohol drinker, lower educational level, and employed status), health-related factors (lower fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin level, good self-perceived health status, more comorbidities, recent health screening, more outpatient visits, and diet therapy), and diabetic factors (more awareness and getting treated) were associated with influenza vaccination. In multivariate analysis, more awareness and getting treated for diabetes were associated with influenza vaccination in diabetic patients under 65 years (odds ratio, 1.496 and 1.413; 95% confidence interval, 1.022 to 2.188 and 1.018 to 2.054, respectively).
Conclusion Influenza vaccination rate was low in diabetic patients under 65 years, especially in those with unawareness and not getting treated for diabetes. Active screening and treatment for diabetes may be helpful to improve the influenza vaccination rate in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adherence to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in diabetes mellitus patients in Saudi Arabia: A multicenter retrospective study
Saleh Fahad Alqifari, Aya K Esmail, Dalal M Alarifi, Ghalya Y Alsuliman, Maram M Alhati, May R Mutlaq, Mohammed Aldhaeefi, Shaden A Alshuaibi, Palanisamy Amirthalingam, Abrar Abdallah, Afaf S Wasel, Heba R Hamad, Shoroq Alamin, Tasneem H Atia, Tariq Alqah
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 440. CrossRef - ЕГДЕ ЖАСТАҒЫ АДАМДАРДА COVID-19 ВАКЦИНАЦИЯСЫНЫҢ ТИІМДІЛІГІ
Ю.Р. АБДУСАТТАРОВА, Д.С. ӘБЕН, Н. АБДОЛЛА, Р.Т. ТЛЕУЛИЕВА, А. КАЛИ, Ю.В. ПЕРФИЛЬЕВА
Vestnik.2023; (2(65)): 59. CrossRef - Comorbidities associated with high-risk obstructive sleep apnea based on the STOP-BANG questionnaire: a nationwide population-based study
Gene Huh, Kyoung do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Chan-Soon Park, Kyu-na Lee, Eun Young Lee, Jung-Hae Cho
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 80. CrossRef - Influenza vaccination trend and related factors among patients with diabetes in Korea: Analysis using a nationwide database
Dong-Hwa Lee, Bumhee Yang, Seonhye Gu, Eung-Gook Kim, Youlim Kim, Hyung Koo Kang, Yeong Hun Choe, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Seungyong Park, Hyun Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with seasonal influenza immunization in people with chronic diseases
Slađana Arsenović, Tatjana Gazibara
Medicinski podmladak.2021; 72(2): 19. CrossRef
- Adherence to Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices in diabetes mellitus patients in Saudi Arabia: A multicenter retrospective study
- Epidemiology
- Associations between Breastfeeding and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Glycemic Control in Parous Women: A Nationwide, Population-Based Study
- Ga Eun Nam, Kyungdo Han, Do-Hoon Kim, Youn Huh, Byoungduck Han, Sung Jung Cho, Yong Gyu Park, Yong-Moon Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):236-241. Published online December 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0044
- 4,037 View
- 45 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader We investigated associations between breastfeeding duration and number of children breastfed and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and glycemic control among parous women. We performed a cross-sectional analysis of data for 9,960 parous women from the Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey (2010 to 2013). Having ever breastfed was inversely associated with prevalent T2DM (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.60; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.42 to 0.87). All ranges of total and average breastfeeding duration showed inverse associations with T2DM. Even short periods of breastfeeding were inversely associated with T2DM (adjusted OR, 0.61; 95% CI, 0.38 to 0.99 for a total breastfeeding duration ≤12 months; adjusted OR, 0.65; 95% CI, 0.42 to 0.99 for an average breastfeeding duration per child ≤6 months). A longer duration of breastfeeding was associated with better glycemic control in parous women with T2DM (
P trend=0.004 for total breastfeeding duration;P trend <0.001 for average breastfeeding duration per child). Breastfeeding may be associated with a lower risk of T2DM and good glycemic control in parous women with T2DM. Breastfeeding may be a feasible method to prevent T2DM and improve glycemic control.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of nutrigenomics, melatonin, serotonin and inflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Danielle Cristina Honorio França, Eduardo Luzía França, Luis Sobrevia, Angélica Mércia Pascon Barbosa, Adenilda Cristina Honorio-França, Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2023; 1869(6): 166737. CrossRef - Association of lactation with maternal risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of observational studies
Ana‐Catarina Pinho‐Gomes, Georgia Morelli, Alexandra Jones, Mark Woodward
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(8): 1902. CrossRef - Updates in Gestational Diabetes Prevalence, Treatment, and Health Policy
Laura T. Dickens, Celeste C. Thomas
Current Diabetes Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Integration of nutrigenomics, melatonin, serotonin and inflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
- Complications
- Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Higher HbA1c Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yeoree Yang, Eun-Young Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Seung-Hwan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):496-512. Published online September 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0026
- 4,267 View
- 42 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to investigate the association between the presence and severity of cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy (CAN) and development of long-term glucose fluctuation in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods In this retrospective cohort study, subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus who received cardiovascular autonomic reflex tests (CARTs) at baseline and at least 4-year of follow-up with ≥6 measures of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were included. The severity of CAN was categorized as normal, early, or severe CAN according to the CARTs score. HbA1c variability was measured as the standard deviation (SD), coefficient of variation, and adjusted SD of serial HbA1c measurements.
Results A total of 681 subjects were analyzed (294 normal, 318 early, and 69 severe CAN). The HbA1c variability index values showed a positive relationship with the severity of CAN. Multivariable logistic regression analysis showed that CAN was significantly associated with the risk of developing higher HbA1c variability (SD) after adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, diabetes duration, mean HbA1c, heart rate, glomerular filtration rate, diabetic retinopathy, coronary artery disease, insulin use, and anti-hypertensive medication (early CAN: odds ratio [OR], 1.65; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.12 to 2.43) (severe CAN: OR, 2.86; 95% CI, 1.47 to 5.56). This association was more prominent in subjects who had a longer duration of diabetes (>10 years) and lower mean HbA1c (<7%).
Conclusion CAN is an independent risk factor for future higher HbA1c variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Tailored therapy for stabilizing glucose fluctuation should be emphasized in subjects with CAN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intensified glycemic control by HbA1c for patients with coronary heart disease and Type 2 diabetes: a review of findings and conclusions
Jingyang Chen, Dong Yin, Kefei Dou
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients According to Average and Visit-to-Visit Variations of HbA1c Levels During the First 3 Years of Diabetes Diagnosis
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Associated with Diabetic Complication Index among Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Focusing on Regular Outpatient Follow-up and HbA1c Variability
Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Asian Nursing Research.2023; 17(5): 259. CrossRef - The Association of Postprandial Triglyceride Variability with Renal Dysfunction and Microalbuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetic Mellitus: A Retrospective and Observational Study
Natsumi Matsuoka-Uchiyama, Haruhito A. Uchida, Shugo Okamoto, Yasuhiro Onishi, Katsuyoshi Katayama, Mariko Tsuchida-Nishiwaki, Hidemi Takeuchi, Rika Takemoto, Yoshiko Hada, Ryoko Umebayashi, Naoko Kurooka, Kenji Tsuji, Jun Eguchi, Hirofumi Nakajima, Kenic
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Perspectives of glycemic variability in diabetic neuropathy: a comprehensive review
Xiaochun Zhang, Xue Yang, Bao Sun, Chunsheng Zhu
Communications Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of Functions of the Autonomic Nervous System in the Elderly with Different Comorbid Factors
Sushma S., Medha Y. Rao, Shaikh Mohammed Aslam
Journal of Neurosciences in Rural Practice.2020; 12: 80. CrossRef - Prognostic irrelevance of plaque vulnerability following plaque sealing in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes: an optical coherence tomography study
Rosalia Dettori, Andrea Milzi, Kathrin Burgmaier, Mohammad Almalla, Martin Hellmich, Nikolaus Marx, Sebastian Reith, Mathias Burgmaier
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - HbA1C Variability Is Strongly Associated With the Severity of Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes After Longer Diabetes Duration
Yun-Ru Lai, Chih-Cheng Huang, Wen-Chan Chiu, Rue-Tsuan Liu, Nai-Wen Tsai, Hung-Chen Wang, Wei-Che Lin, Ben-Chung Cheng, Yu-Jih Su, Chih-Min Su, Sheng-Yuan Hsiao, Pei-Wen Wang, Jung-Fu Chen, Cheng-Hsien Lu
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Polyscore of Non-invasive Cardiac Risk Factors
Alexander Steger, Alexander Müller, Petra Barthel, Michael Dommasch, Katharina Maria Huster, Katerina Hnatkova, Daniel Sinnecker, Alexander Hapfelmeier, Marek Malik, Georg Schmidt
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Intensified glycemic control by HbA1c for patients with coronary heart disease and Type 2 diabetes: a review of findings and conclusions
- Epidemiology
- Serum Betatrophin Concentrations and the Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Nested Case-Control Study from Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Marie Rhee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(1):53-62. Published online November 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.53
- 3,600 View
- 52 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Betatrophin is a newly identified hormone derived from the liver and adipose tissue, which has been suggested to regulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Circulating levels of betatrophin are altered in various metabolic diseases, although the results are inconsistent. We aimed to examine whether betatrophin is a useful biomarker in predicting the development of diabetes.
Methods A nested case-control study was performed using a prospective Chungju Metabolic disease Cohort Study. During a 4-year follow-up period, we analyzed 167 individuals who converted to diabetes and 167 non-converters, who were matched by age, sex, and body mass index. Serum betatrophin levels were measured by an ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
Results Baseline serum betatrophin levels were significantly higher in the converter group compared to the non-converter group (1,315±598 pg/mL vs. 1,072±446 pg/mL,
P <0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, fasting plasma glucose, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and family history of diabetes, the risk of developing diabetes showed a stepwise increase across the betatrophin quartile groups. Subjects in the highest baseline quartile of betatrophin levels had more than a threefold higher risk of incident diabetes than the subjects in the lowest quartile (relative risk, 3.275; 95% confidence interval, 1.574 to 6.814;P =0.010). However, no significant relationships were observed between serum betatrophin levels and indices of insulin resistance or β-cell function.Conclusion Circulating levels of betatrophin could be a potential biomarker for predicting new-onset diabetes. Further studies are needed to understand the underlying mechanism of this association.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal and cord blood betatrophin (angiopoietin‐like protein 8) in pregnant women with gestational diabetes and normoglycemic controls: A systematic review, meta‐analysis, and meta‐regression
Faustino R. Pérez‐López, Junhua Yuan, Manuel Sánchez‐Prieto, María T. López‐Baena, Gonzalo R. Pérez‐Roncero, Seshadri Reddy Varikasuvu
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Adiponectin and ANGPTL8 in Women With Metabolic Syndrome in the Madinah Region of Saudi Arabia
Walaa Mohammedsaeed, Ahmed Ahmed, Nada Alharbi, Amjaad Aljohani, Razan Alruwaithi, Reem Alharbi, Shatha Alahmadi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Betatrophin with Irisin and Metabolic Factors: Effects of Two Exercise Trainings in Diabetic Rats
Hassan Tavassoli, Ali Heidarianpour
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 496. CrossRef - Evidences for Expression and Location of ANGPTL8 in Human Adipose Tissue
Leonardo Catalano-Iniesta, Virginia Sánchez Robledo, María Carmen Iglesias-Osma, Amparo Galán Albiñana, Sixto Carrero, Enrique J. Blanco, Marta Carretero-Hernández, José Carretero, María José García-Barrado
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 512. CrossRef - Higher circulating levels of ANGPTL8 are associated with body mass index, triglycerides, and endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease
Reza Fadaei, Hossein Shateri, Johanna K. DiStefano, Nariman Moradi, Mohammad Mohammadi, Farzad Emami, Hassan Aghajani, Nasrin Ziamajidi
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2020; 469(1-2): 29. CrossRef - Effects of a diet with or without physical activity on angiopoietin-like protein 8 concentrations in overweight/obese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Hao Hu, Guoyue Yuan, Xinchen Wang, Jin Sun, Zhaohua Gao, Tingting Zhou, Wenwen Yin, Ruonan Cai, Xing Ye, Zhaoling Wang
Endocrine Journal.2019; 66(1): 89. CrossRef - The potential role of angiopoietin-like protein-8 in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a possibility for predictive diagnosis and targeted preventive measures?
Yasmine Amr Issa, Samar Samy Abd ElHafeez, Noha Gaber Amin
EPMA Journal.2019; 10(3): 239. CrossRef - A Short Review on ANGPTL-8 as an Important Regulator in Diabetes
Maryam Esfahani, Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi
Avicenna Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2019; 7(2): 61. CrossRef
- Maternal and cord blood betatrophin (angiopoietin‐like protein 8) in pregnant women with gestational diabetes and normoglycemic controls: A systematic review, meta‐analysis, and meta‐regression
- Complications
- Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
- Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):482-493. Published online October 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.482
- 4,536 View
- 63 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 34 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated clinical course and risk factors for diabetic retinopathy (DR) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods A total of 759 patients with T2DM without DR were included from January 2001 to December 2004. Retinopathy evaluation was performed at least annually by ophthalmologists. The severity of the DR was classified into five categories according to the International Clinical Diabetic Retinopathy Severity Scales.
Results Of the 759 patients, 523 patients (68.9%) completed the follow-up evaluation. During the follow-up period, 235 patients (44.9%) developed DR, and 32 patients (13.6%) progressed to severe nonproliferative DR (NPDR) or proliferative DR (PDR). The mean duration of diabetes at the first diagnosis of mild NPDR, moderate NPDR, and severe NPDR or PDR were 14.8, 16.7, and 17.3 years, respectively. After adjusting multiple confounding factors, the significant risk factors for the incidence of DR risk in patients with T2DM were old age, longer duration of diabetes, higher mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and albuminuria. Even in the patients who had been diagnosed with diabetes for longer than 10 years at baseline, a decrease in HbA1c led to a significant reduction in the risk of developing DR (hazard ratio, 0.73 per 1% HbA1c decrement; 95% confidence interval, 0.58 to 0.91;
P =0.005).Conclusion This prospective cohort study demonstrates that glycemic control, diabetes duration, age, and albuminuria are important risk factors for the development of DR. More aggressive retinal screening for T2DM patients diagnosed with DR should be required in order to not miss rapid progression of DR.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of diabetes and its correlates among Iranian adults: Results of the first phase of Shahedieh cohort study
Ali Dehghani, Hamid Korozhdehi, Saeid Hossein Khalilzadeh, Hossein Fallahzadeh, Vahid Rahmanian
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based fundus image analysis for cardiovascular disease: a review
Symon Chikumba, Yuqian Hu, Jing Luo
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of anticoagulant/antiplatelet therapy on the development and progression of diabetic retinopathy
Chi-Juei Jeng, Yi-Ting Hsieh, Cheng-Li Lin, I-Jong Wang
BMC Ophthalmology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A deep learning model for screening type 2 diabetes from retinal photographs
Jae-Seung Yun, Jaesik Kim, Sang-Hyuk Jung, Seon-Ah Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn, Hong-Hee Won, Kyung-Ah Sohn, Dokyoon Kim
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(5): 1218. CrossRef - Risk factor analysis and clinical decision tree model construction for diabetic retinopathy in Western China
Yuan-Yuan Zhou, Tai-Cheng Zhou, Nan Chen, Guo-Zhong Zhou, Hong-Jian Zhou, Xing-Dong Li, Jin-Rui Wang, Chao-Fang Bai, Rong Long, Yu-Xin Xiong, Ying Yang
World Journal of Diabetes.2022; 13(11): 986. CrossRef - Association of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Dis-ease and Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Cross-Sectional Study
Zahra Heidari, Zahra Sharafi
Iranian South Medical Journal.2022; 25(1): 30. CrossRef - The Related Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Hospital-Based Cohort Study in Taiwan
Tsai-Tung Chiu, Tien-Lung Tsai, Mei-Yin Su, Tsan Yang, Peng-Lin Tseng, Yau-Jiunn Lee, Chao-Hsien Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(1): 307. CrossRef - Association of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetic patients: A meta‐analysis of observational studies
Dandan Song, Chengqian Li, Zhongchao Wang, Yuhang Zhao, Baoming Shen, Wenjuan Zhao
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(8): 1471. CrossRef - PREVALENCE OF ADVANCED DIABETIC EYE DISEASE AND ITS ASSOCIATED RISK FACTORS IN TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Likathung Ngullie, Bratatee Roy, Sayantan Ghosh, Sneha Jain, Lakshmi Kanta Mondal
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 25. CrossRef - Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy and Declining Renal Function in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
AJin Cho, Hayne Cho Park, Young-Ki Lee, Young Joo Shin, So Hyun Bae, Hakyoung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - First nation-wide study of diabetic retinopathy in Poland in the years 2013–2017
Milena Kozioł, Michał S. Nowak, Monika Udziela, Paweł Piątkiewicz, Iwona Grabska-Liberek, Jacek P. Szaflik
Acta Diabetologica.2020; 57(10): 1255. CrossRef - Awareness of diabetic retinopathy among Saudis with diabetes type 2 in Riyadh city
YousefM Alluhaymid, FawzanY Alotaibi, AbdulmajeedB Alotaibi, AbdullahM Albasha, AbdulrahmanS Alnaim, EssaM Sabi, AhmedH Mujamammi
Journal of Family Medicine and Primary Care.2020; 9(8): 4229. CrossRef - Relationship between Clinical Features of Diabetic Retinopathy and Systemic Factors in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type II Diabetes Mellitus
Hyeseong Hwang, Jin Young Kim, Tae Keun Oh, Ju Byung Chae, Dong Yoon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Longitudinal Screening for Diabetic Retinopathy in a Nationwide Screening Program: Comparing Deep Learning and Human Graders
Jirawut Limwattanayingyong, Variya Nganthavee, Kasem Seresirikachorn, Tassapol Singalavanija, Ngamphol Soonthornworasiri, Varis Ruamviboonsuk, Chetan Rao, Rajiv Raman, Andrzej Grzybowski, Mike Schaekermann, Lily H. Peng, Dale R. Webster, Christopher Semtu
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Protective factors for diabetic retinopathy in Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: Long duration of no less than 10 years
Yanli Liu, Chunwen Duan, Dejia Fang, Yi Liu, Hanchun Xu, Yarong Zheng, Yaling Xuan, Lili Wang, Lin Ye, Rui Su, Meixia An
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(10): 107383. CrossRef - Incidence of sight‐threatening diabetic retinopathy in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus and numbers needed to screen: a systematic review
Y. Groeneveld, D. Tavenier, J.W. Blom, B.C.P. Polak
Diabetic Medicine.2019; 36(10): 1199. CrossRef - Association between spousal diabetes status and diabetic retinopathy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Mei Yang, Yu Liu, Cuihong Wen, Beirui Wu, Xu Wan, Wei Luan, Jie Shen, Wei Liu, Jing Ma
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2019; 16(5): 474. CrossRef - Presence of diabetic retinopathy is lower in type 2 diabetic patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Meng Zhang, Li Li, Jing Chen, Bei Li, Yutao Zhan, Chuan Zhang
Medicine.2019; 98(18): e15362. CrossRef - MicroRNAs as biomarkers of diabetic retinopathy and disease progression
Bridget Martinez, PhilipV Peplow
Neural Regeneration Research.2019; 14(11): 1858. CrossRef - Vascular changes in diabetic retinopathy—a longitudinal study in the Nile rat
Huishi Toh, Alexander Smolentsev, Rachel V. Bozadjian, Patrick W. Keeley, Madison D. Lockwood, Ryan Sadjadi, Dennis O. Clegg, Barbara A. Blodi, Peter J. Coffey, Benjamin E. Reese, James A. Thomson
Laboratory Investigation.2019; 99(10): 1547. CrossRef - DIABETE, TABAGISMO E DISASSUEFAZIONE DAL FUMO
Davide Campagna, Angela Alamo, Enrico Mondati, Riccardo Polosa
il Diabete.2019; 31(N. 1, marz): 41. CrossRef - Smoking and diabetes: dangerous liaisons and confusing relationships
D. Campagna, A. Alamo, A. Di Pino, C. Russo, A. E. Calogero, F. Purrello, R. Polosa
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors versus Other Antidiabetic Drugs Added to Metformin Monotherapy in Diabetic Retinopathy Progression: A Real World-Based Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:640–8)
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 911. CrossRef - Past and Current Status of Adult Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Management in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Yong-ho Lee, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Dae-Jung Kim, Chang Hee Jung, Ki-Up Lee, Kyung-Soo Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(2): 93. CrossRef - Excess visceral adiposity is associated with diabetic retinopathy in a multiethnic Asian cohort with longstanding type 2 diabetes
Angela Moh, Kumari Neelam, Xiao Zhang, Chee Fang Sum, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Keven Ang, Simon Biing Ming Lee, Wern Ee Tang, Su Chi Lim
Endocrine Research.2018; 43(3): 186. CrossRef - RNA sequencing identified specific circulating miRNA biomarkers for early detection of diabetes retinopathy
Zhen Liang, Kai P. Gao, Yi X. Wang, Zi C. Liu, Li Tian, Xin Z. Yang, Jing Y. Ding, Wei T. Wu, Wen H. Yang, Yi L. Li, Ze B. Zhang, Ri H. Zhai
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 315(3): E374. CrossRef - High hemoglobin levels are associated with decreased risk of diabetic retinopathy in Korean type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jee-Sun Jeong, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Cigarette Smoking, Diabetes, and Diabetes Complications: Call for Urgent Action
Ping Zhu, Xiong-Fei Pan, Liting Sheng, Henggui Chen, An Pan
Current Diabetes Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:393-404)
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeong-Taek Woo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 494. CrossRef - Letter: Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea (Diabetes Metab J2016;40:482-93)
Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 75. CrossRef - Combined treatment of diabetic nephropathy with alprostadil and calcium dobesilate
Lili Qin, Wenjun Qin, Jianfei Wang, Lin Lin
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea (Diabetes Metab J2016;40:482-93)
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 77. CrossRef - Clinical characteristics and risk factors for retinal diabetic neurodegeneration in type 2 diabetes
Kiyoung Kim, Eung Suk Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, Jeong-taek Woo, Seung-Young Yu
Acta Diabetologica.2017; 54(11): 993. CrossRef - Letter: Features of Long-Standing Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy: A Study Based on Standardized Clinical Data (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:393-404)
Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 492. CrossRef
- Prevalence of diabetes and its correlates among Iranian adults: Results of the first phase of Shahedieh cohort study
- Complications
- Baseline-Corrected QT (QTc) Interval Is Associated with Prolongation of QTc during Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Yoon-Goo Kang, Kang-Min Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):463-472. Published online October 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.463
- 3,669 View
- 47 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated an association between baseline heart rate-corrected QT (QTc) interval before severe hypoglycemia (SH) and prolongation of QTc interval during SH in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods Between January 2004 and June 2014, 208 patients with T2DM, who visited the emergency department because of SH and underwent standard 12-lead electrocardiography within the 6-month period before SH were consecutively enrolled. The QTc interval was analyzed during the incidence of SH, and 6 months before and after SH. QTc intervals of 450 ms or longer in men and 460 ms or longer in women were considered abnormally prolonged.
Results The mean age and diabetes duration were 68.1±12.1 and 14.1±10.1 years, respectively. The mean QTc intervals at baseline and SH episodes were 433±33 and 460±33 ms, respectively (
P <0.001). One hundred and fourteen patients (54.8%) had a prolonged QTc interval during SH. There was a significant decrease in the prolonged QTc interval within 6 months after SH (QTc interval prolongation during SH vs. after recovery, 54.8% vs. 33.8%,P <0.001). The prolonged QTc interval was significantly associated with baseline QTc interval prolongation (odds ratio, 2.92; 95% confidence interval, 1.22 to 6.96;P =0.016) after adjusting for multiple confounders.Conclusion A prolonged QTc interval at baseline was significantly associated with prolongation of the QTc interval during SH in patients with T2DM, suggesting the necessity of QTc interval monitoring and attention to those with a prolonged QTc interval to prevent SH.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prevalence of QT prolongation and its risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Khaled Aburisheh, Mohammad F. AlKheraiji, Saleh I. Alwalan, Arthur C. Isnani, Mohamed Rafiullah, Muhammad Mujammami, Assim A. Alfadda
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - U-shaped association between the triglyceride–glucose index and atrial fibrillation incidence in a general population without known cardiovascular disease
Xiao Liu, Ayiguli Abudukeremu, Yuan Jiang, Zhengyu Cao, Maoxiong Wu, Jianyong Ma, Runlu Sun, Wanbing He, Zhiteng Chen, Yangxin Chen, Peng Yu, Wengen Zhu, Yuling Zhang, Jingfeng Wang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Celebrities in the heart, strangers in the pancreatic beta cell: Voltage‐gated potassium channels Kv7.1 and Kv11.1 bridge long QT syndrome with hyperinsulinaemia as well as type 2 diabetes
Anniek F. Lubberding, Christian R. Juhl, Emil Z. Skovhøj, Jørgen K. Kanters, Thomas Mandrup‐Poulsen, Signe S. Torekov
Acta Physiologica.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Heart rate-corrected QT interval prolongation is associated with decreased heart rate variability in patients with type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha
Medicine.2022; 101(45): e31511. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Soo-Yeon Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 263. CrossRef - Review of the cardiovascular safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the clinical relevance of the CAROLINA trial
Marile Santamarina, Curt J. Carlson
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Antioxidant effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the aTC1-6 pancreatic alpha cell line
Ting Cao, Xiong Zhang, Dan Yang, Yue-Qian Wang, Zheng-Dong Qiao, Jian-Ming Huang, Peng Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 495(1): 693. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Nationwide population-based cohort study
Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Eue-Keun Choi, Kyungdo Han, Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(2): 157. CrossRef - Incidence of prolonged QTc and severe hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: the EURODIAB Prospective Complications Study
Cristina Amione, Sara Giunti, Paolo Fornengo, Sabita S. Soedamah-Muthu, Nish Chaturvedi, J. H. Fuller, Federica Barutta, Gabriella Gruden, Graziella Bruno
Acta Diabetologica.2017; 54(9): 871. CrossRef
- Prevalence of QT prolongation and its risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Complications
- Severe Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular or All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seawon Hwang, Eun-Jung Yim, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(3):202-210. Published online April 5, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.3.202
- 4,458 View
- 60 Download
- 49 Web of Science
- 57 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the association between severe hypoglycemia (SH) and the risk of cardiovascular (CV) or all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods The study included 1,260 patients aged 25 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes from the Vincent Type 2 Diabetes Resgistry (VDR), who consecutively enrolled (
n =1,260) from January 2000 to December 2010 and were followed up until May 2015 with a median follow-up time of 10.4 years. Primary outcomes were death from any cause or CV death. We investigated the association between the CV or all-cause mortality and various covariates using Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.Results Among the 906 participants (71.9%) who completed follow-up, 85 patients (9.4%) had at least one episode of SH, and 86 patients (9.5%) died (9.1 per 1,000 patient-years). Patients who had died were older, had a longer duration of diabetes and hypertension, received more insulin, and had more diabetic microvascular complications at baseline, as compared with surviving patients. The experience of SH was significantly associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.39 to 5.02;
P =0.003) and CV mortality (HR, 6.34; 95% CI, 2.02 to 19.87;P =0.002) after adjusting for sex, age, diabetic duration, hypertension, mean glycosylated hemoglobin levels, diabetic nephropathy, lipid profiles, and insulin use.Conclusion We found a strong association between SH and increased risk of all-cause and CV mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The prognostic value of the stress hyperglycemia ratio for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with diabetes or prediabetes: insights from NHANES 2005–2018
Lei Ding, Hongda Zhang, Cong Dai, Aikai Zhang, Fengyuan Yu, Lijie Mi, Yingjie Qi, Min Tang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating the future of diabetes: innovative nomogram models for predicting all-cause mortality risk in diabetic nephropathy
Sensen Wu, Hui Wang, Dikang Pan, Julong Guo, Fan Zhang, Yachan Ning, Yongquan Gu, Lianrui Guo
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of hypoglycaemia with the risks of arrhythmia and mortality in individuals with diabetes - a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gangfeng Li, Shuping Zhong, Xingmu Wang, Fuyuan Zhuge
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus und Straßenverkehr – ein Positionspapier der Österreichischen Diabetesgesellschaft (Update 2023)
Heidemarie Abrahamian, Birgit Salamon, Angelika Lahnsteiner, Christian Schelkshorn, Alexander Bräuer, Lars Stechemesser, Gerd Köhler, Martin Clodi
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(S1): 319. CrossRef - Validation of the hypoglycemia awareness questionnaire to assess hypoglycemia awareness in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin
Diana Cristina Henao-Carrillo, Fabio Alexander Sierra-Matamoros, Ana Julia Carrillo Algarra, Julieth Patricia García-Lugo, Sandra Milena Hernández-Zambrano
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(12): 102917. CrossRef - Basal insulin analogues in people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease
David León‐Jiménez, José Pablo Miramontes‐González, Laura Márquez‐López, Francisco Astudillo‐Martín, Luis M. Beltrán‐Romero, Fernando Moreno‐Obregón, Javier Escalada‐San Martín
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe Hypoglycemia Increases Dementia Risk and Related Mortality: A Nationwide, Population-based Cohort Study
Eugene Han, Kyung-do Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): e1976. CrossRef - Validación transcultural del HypoA-Q para medir conciencia de hipoglucemia en pacientes diabéticos
Ana Julia Carrillo-Algarra, Sandra Milena Hernandez-Zambrano, Fabio Alexander Sierra-Matamoros, Diana Cristina Henao-Carrillo, Ana María Gómez-Medina, Daniel Esteban Hurtado-Barrera
Revista Ciencia y Cuidado.2022; 19(1): 42. CrossRef - Validity of the diagnosis of diabetic microvascular complications in Korean national health insurance claim data
Hyung Jun Kim, Moo-Seok Park, Jee-Eun Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Annals of Clinical Neurophysiology.2022; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Clinical Platform to Promote Chronic Disease Management
Laura Greene, Nila Sathe, John A. House, Laura L. Schott, Stella Safo
Population Health Management.2021; 24(4): 470. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Soo-Yeon Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 263. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis: Association Between Hypoglycemia and Serious Adverse Events in Older Patients Treated With Glucose-Lowering Agents
Katharina Mattishent, Yoon K. Loke
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology and outcomes from severe hypoglycemia in Kuwait: a prospective cohort study
Dalal Al Hasan, Ameen Yaseen, Mohammad Al Roudan, Lee Wallis
BMC Emergency Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The incidence of hypoglycemia and its risk factors among diabetic patients in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
Ahmed Elshebiny, Hassan Alali, Zainab Alamer, Yasmin Alsultan, Hashim Alkhalaf, Abdullah Alkishi, Mohammed Alsuwaylih
International Journal of Medicine in Developing Countries.2021; : 614. CrossRef - Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154838. CrossRef - Real-world Evaluation of glycemic control and hypoglycemic Events among type 2 Diabetes mellitus study (REEDS): a multicentre, cross-sectional study in Thailand
Bancha Satirapoj, Thongchai Pratipanawatr, Boonsong Ongphiphadhanakul, Sompongse Suwanwalaikorn, Yupin Benjasuratwong, Wannee Nitiyanant
BMJ Open.2020; 10(2): e031612. CrossRef Predictors of Diabetes Self-Care Practice Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Public Hospitals in Northeastern Ethiopia: A Facility-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Tesfaye Molla Gulentie, Ebrahim Mohammed Yesuf, Taklo Simeneh Yazie, Belayneh Kefale
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 3137. CrossRef- Hypoglycemia in Older Patients
Byron J. Hoogwerf
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2020; 36(3): 395. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycaemia and absolute risk of cause-specific mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a UK primary care observational study
Francesco Zaccardi, Suping Ling, Claire Lawson, Melanie J. Davies, Kamlesh Khunti
Diabetologia.2020; 63(10): 2129. CrossRef - Insulin Glargine U100 Improved Glycemic Control and Reduced Nocturnal Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4
Carolina C. Betônico, Silvia Maria O. Titan, Aécio Lira, Tatiana S. Pelaes, Maria Lúcia C. Correa-Giannella, Márcia Nery, Márcia Queiroz
Clinical Therapeutics.2019; 41(10): 2008. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Degludec Compared to Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Experienced Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Trial Protocol Amendment (NCT03078478)
Athena Philis-Tsimikas, Irene Stratton, Lone Nørgård Troelsen, Britta Anker Bak, Lawrence A. Leiter
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2019; 13(3): 498. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of insulin glargine/lixisenatide (iGlarLixi) fixed-ratio combination in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Yehuda Handelsman, Christina Chovanes, Terry Dex, Francesco Giorgino, Neil Skolnik, Elisabeth Souhami, William Stager, Elisabeth Niemoeller, Juan Pablo Frias
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 236. CrossRef - Urinary glucose excretion after dapagliflozin treatment: An exposure‐response modelling comparison between Japanese and non‐Japanese patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Victor Sokolov, Tatiana Yakovleva, Shinya Ueda, Joanna Parkinson, David W. Boulton, Robert C. Penland, Weifeng Tang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(4): 829. CrossRef - Effects on clinical outcomes of intensifying triple oral antidiabetic drug (OAD) therapy by initiating insulin versus enhancing OAD therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population‐based, propensity‐score‐matched cohort study
Shihchen Kuo, Chun‐Ting Yang, Jin‐Shang Wu, Huang‐Tz Ou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(2): 312. CrossRef - Cardiovascular safety and lower severe hypoglycaemia of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 65 years or older: Results from DEVOTE (DEVOTE 7)
Richard E. Pratley, Scott S. Emerson, Edward Franek, Matthew P. Gilbert, Steven P. Marso, Darren K. McGuire, Thomas R. Pieber, Bernard Zinman, Charlotte T. Hansen, Melissa V. Hansen, Thomas Mark, Alan C. Moses, John B. Buse
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(7): 1625. CrossRef - Review of the cardiovascular safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the clinical relevance of the CAROLINA trial
Marile Santamarina, Curt J. Carlson
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 12-week moderate-intensity exercise training on blood glucose response in patients with type 2 diabetes
Shang-Lin Chiang, Margaret McLean Heitkemper, Yi-Jen Hung, Wen-Chii Tzeng, Meei-Shyuan Lee, Chia-Huei Lin
Medicine.2019; 98(36): e16860. CrossRef - Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycaemia in Insulin-treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohammad J. Alkhatatbeh, Nedaa A. Abdalqader , Mohammad A.Y. Alqudah
Current Diabetes Reviews.2019; 15(5): 407. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in diabetes: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management
Stephanie A Amiel, Pablo Aschner, Belinda Childs, Philip E Cryer, Bastiaan E de Galan, Brian M Frier, Linda Gonder-Frederick, Simon R Heller, Timothy Jones, Kamlesh Khunti, Lawrence A Leiter, Yingying Luo, Rory J McCrimmon, Ulrik Pedersen-Bjergaard, Eliza
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2019; 7(5): 385. CrossRef - Sulfonylureas as initial treatment for type 2 diabetes and the risk of adverse cardiovascular events: A population‐based cohort study
Kristian B. Filion, Antonios Douros, Laurent Azoulay, Hui Yin, Oriana H. Yu, Samy Suissa
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2019; 85(10): 2378. CrossRef - Selectivity of beta-blockers, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in people with hypoglycaemia: An observational study
F. Zaccardi, L.L. Nystrup Husemoen, B.L. Thorsted, D.R. Webb, S.K. Paul, M.J. Davies, K. Khunti
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2019; 29(5): 481. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of a primary care multidisciplinary Risk Assessment and Management Program for patients with diabetes mellitus (RAMP-DM) over lifetime
Fangfang Jiao, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Anca Ka Chun Chan, Sarah Morag McGhee, Ruby Lai Ping Kwok, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Endocrine.2019; 63(2): 259. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAPT) with predictive low-glucose management in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus previously treated with SAPT and low glucose suspend
Ana María Gómez, Diana Cristina Henao, Angelica Imitola, Oscar Mauricio Muñoz, Martín Alonso Rondón Sepúlveda, Laura Kattah, Juan Sebastian Guerrero, Elly Morros, Juan Pablo Llano, Maira García Jaramillo, Fabián León-Vargas
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2018; 65(8): 451. CrossRef - Recent diabetes-related mortality trends in Romania
Sorin Ioacara, Elisabeta Sava, Olivia Georgescu, Anca Sirbu, Simona Fica
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(8): 821. CrossRef - Use of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors from clinical trial results to practical application in Russia
D. A. Lebedev, A. Yu. Babenko
Medical Council.2018; (16): 100. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Nationwide population-based cohort study
Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Eue-Keun Choi, Kyungdo Han, Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(2): 157. CrossRef - Antioxidant effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the aTC1-6 pancreatic alpha cell line
Ting Cao, Xiong Zhang, Dan Yang, Yue-Qian Wang, Zheng-Dong Qiao, Jian-Ming Huang, Peng Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 495(1): 693. CrossRef - Hemoglobin glycation index predicts cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10-year longitudinal cohort study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Jee Sun Jeong, Jae-Seung Yun, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(10): 906. CrossRef - Day-to-day fasting glycaemic variability in DEVOTE: associations with severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular outcomes (DEVOTE 2)
Bernard Zinman, Steven P. Marso, Neil R. Poulter, Scott S. Emerson, Thomas R. Pieber, Richard E. Pratley, Martin Lange, Kirstine Brown-Frandsen, Alan Moses, Ann Marie Ocampo Francisco, Jesper Barner Lekdorf, Kajsa Kvist, John B. Buse
Diabetologia.2018; 61(1): 48. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAPT) with predictive low-glucose management in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus previously treated with SAPT and low glucose suspend
Ana María Gómez, Diana Cristina Henao, Angelica Imitola, Oscar Mauricio Muñoz, Martín Alonso Rondón Sepúlveda, Laura Kattah, Juan Sebastian Guerrero, Elly Morros, Juan Pablo Llano, Maira García Jaramillo, Fabián León-Vargas
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2018; 65(8): 451. CrossRef - Time- and frequency-domain measures of heart rate variability predict cardiovascular outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hwan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Sung-Rae Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 143: 159. CrossRef - Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in an ethnic minority population: clinical presentation and comparison to other populations
Michael Morkos, Bettina Tahsin, Louis Fogg, Leon Fogelfeld
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2018; 6(1): e000568. CrossRef - DEVOTE 3: temporal relationships between severe hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality
Thomas R. Pieber, Steven P. Marso, Darren K. McGuire, Bernard Zinman, Neil R. Poulter, Scott S. Emerson, Richard E. Pratley, Vincent Woo, Simon Heller, Martin Lange, Kirstine Brown-Frandsen, Alan Moses, Jesper Barner Lekdorf, Lucine Lehmann, Kajsa Kvist,
Diabetologia.2018; 61(1): 58. CrossRef - Intervention effects of Compound Houttuyniae Herba to diabetic renal damage based on SOCS-JAK/STAT negative feedback regulation
Yun Fang, Sai-cong Shao, Hai-ying Wang
Chinese Herbal Medicines.2018; 10(4): 424. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 349. CrossRef - Monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 959. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in diabetic patients with and without established cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Shishi Xu, Xinyue Zhang, Lizhi Tang, Fang Zhang, Nanwei Tong
Postgraduate Medicine.2017; 129(2): 205. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Effects of propofol on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats with type-2 diabetes mellitus
Ying Wang, Xiuru Qi, Chunliang Wang, Danning Zhao, Hongjie Wang, Jianxin Zhang
Biomedical Reports.2017; 6(1): 69. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with diabetes
Marcello Casaccia Bertoluci, Viviane Zorzanelli Rocha
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenetic features of the combined course of arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus 2 type
O.M. Bilovol, L.R. Bobronnikova, O.V. Al-Trawneh
Shidnoevropejskij zurnal vnutrisnoi ta simejnoi medicini.2017; 2017(1): 4. CrossRef - Risk Factors and Adverse Outcomes of Severe Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 423. CrossRef - Real-world evidence for the safety of ipragliflozin in elderly Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (STELLA-ELDER): final results of a post-marketing surveillance study
Koutaro Yokote, Yasuo Terauchi, Ichiro Nakamura, Haruko Sugamori
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2016; 17(15): 1995. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia: Culprit or Bystander?
You-Cheol Hwang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 190. CrossRef - Schwere Hypoglykämien erhöhen die Mortalität
E. Fritschka
MMW - Fortschritte der Medizin.2016; 158(S3): 46. CrossRef
- The prognostic value of the stress hyperglycemia ratio for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with diabetes or prediabetes: insights from NHANES 2005–2018
- Complications
- Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sun-Hye Ko, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(6):498-506. Published online July 8, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.6.498
- 3,225 View
- 34 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate whether a history of prior cardiovascular disease (CVD) is associated with severe hypoglycemia (SH) in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods We conducted a prospective cohort study from January 2001 to December 2012 with a median follow-up time of 9.5 years (5,814 person-years). Patients aged 25 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes and without chronic kidney disease were enrolled (
n =894), and 624 patients completed follow-up. SH was defined as hypoglycemic episodes requiring hospitalization or medical care in an emergency department. We used the Cox proportional hazards regression analysis to test associations between SH episodes and potential explanatory variables.Results Among the 624 participants who completed follow-up, 60 patients (9.6%) had previous CVD. Compared to patients without CVD, patients with previous CVD were older, had a longer duration of diabetes and hypertension, received more insulin, and had more diabetic microvascular complications at baseline. During follow-up, 62 patients (9.9%) experienced at least one SH episode (incidence of 1.33 per 100 patient-years). The development of SH was associated with a history of CVD (hazard ratio, 1.99; 95% confidence interval, 1.07 to 3.72;
P =0.031) after adjusting for sex, age, diabetic duration, hypertension, hemoglobin A1c levels, diabetic complications, cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy, and insulin use.Conclusion A history of CVD was an independent risk factor for the development of SH in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. For patients with CVD, modulation of glycemic targets and diabetic education for the prevention of hypoglycemia should be implemented.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluating the effectiveness of a novel somatostatin receptor 2 antagonist, ZT-01, for hypoglycemia prevention in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes
Ninoschka C. D’Souza, Julian A. Aiken, Emily G. Hoffman, Sara C. Atherley, Sabrina Champsi, Nadia Aleali, Dorsa Shakeri, Maya El-Zahed, Nicky Akbarian, Mehran Nejad-Mansouri, Parinaz Z. Bavani, Richard L. Liggins, Owen Chan, Michael C. Riddell
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Concomitant Use of Sulfonylureas and β-Blockers and the Risk of Severe Hypoglycemia Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Jenny Dimakos, Ying Cui, Robert W. Platt, Christel Renoux, Kristian B. Filion, Antonios Douros
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(2): 377. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of Roxadustat on ventricular repolarization in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis
Yangyang Zhang, Liang Zhang, Pengcheng Ge, Ruyi Xu, Zhen Ye
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathy and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease
Jae-Seung Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 245. CrossRef - Randomised controlled trial of pharmacist-led patient counselling in controlling hypoglycaemic attacks in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (ROSE-ADAM): A study protocol of the SUGAR intervention
Huda Y. Almomani, Carlos Rodriguez Pascual, Sayer I. Al-Azzam, Keivan Ahmadi
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2021; 17(5): 885. CrossRef - Diabetes and Frailty: An Expert Consensus Statement on the Management of Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
W. David Strain, Su Down, Pam Brown, Amar Puttanna, Alan Sinclair
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(5): 1227. CrossRef - Management of hypoglycemia in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Jeffrey Freeman
Postgraduate Medicine.2019; 131(4): 241. CrossRef - Use of stellate ganglion block for treatment of recurrent syncope followed by chest pain
Young-ung Kim, Yong-joon Shin, Young Woo Cho
Yeungnam University Journal of Medicine.2018; 35(1): 104. CrossRef - Coronary artery disease severity modifies associations between glycemic control and both mortality and myocardial infarction
Sridharan Raghavan, Wenhui G. Liu, P. Michael Ho, Mary E. Plomondon, Anna E. Barón, Liron Caplan, Karen E. Joynt Maddox, David Magid, David R. Saxon, Corrine I. Voils, Steven M. Bradley, Thomas M. Maddox
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(5): 480. CrossRef - Depth and combined infection is important predictor of lower extremity amputations in hospitalized diabetic foot ulcer patients
Eun-Gyo Jeong, Sung Shim Cho, Sang-Hoon Lee, Kang-Min Lee, Seo-Kyung Woo, Yoongoo Kang, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Yoon-Jung Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jung-Min Lee
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(5): 952. CrossRef - Time- and frequency-domain measures of heart rate variability predict cardiovascular outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hwan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Sung-Rae Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 143: 159. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Severe Hypoglycemia in Black and White Adults With Diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) Study
Alexandra K. Lee, Clare J. Lee, Elbert S. Huang, A. Richey Sharrett, Josef Coresh, Elizabeth Selvin
Diabetes Care.2017; 40(12): 1661. CrossRef - Early inner retinal thinning and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
Jin A. Choi, Hyo Won Kim, Jin-Woo Kwon, Yun-sub Shim, Dong Hyun Jee, Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn, Chan Kee Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Patrice E. Fort
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(3): e0174377. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Autonomic Dysfunction Predicts Diabetic Foot Ulcers in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Without Diabetic Polyneuropathy
Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Tae-Seok Lim, Eun-Young Lee, Ki-Ho Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Dong Yoo, Joon-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Medicine.2016; 95(12): e3128. CrossRef - Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 482. CrossRef - Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Recurrent Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Kyoungil Min, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, James M Wright
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(10): e0164807. CrossRef - Meta-analysis: Association between hypoglycaemia and serious adverse events in older patients
Katharina Mattishent, Yoon Kong Loke
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(5): 811. CrossRef - Letter: Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:498-506)
Mi-Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(1): 83. CrossRef - Response: Cardiovascular Disease Predicts Severe Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes (Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:498-506)
Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(1): 85. CrossRef - Lipoprotein(a) predicts a new onset of chronic kidney disease in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus
J.‐S. Yun, Y.‐B. Ahn, K.‐H. Song, K.‐D. Yoo, Y.‐M. Park, H.‐W. Kim, S.‐H. Ko
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(5): 639. CrossRef - Severe Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetes
Hyeong Kyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(6): 478. CrossRef
- Evaluating the effectiveness of a novel somatostatin receptor 2 antagonist, ZT-01, for hypoglycemia prevention in a rodent model of type 2 diabetes
- Intensive Individualized Reinforcement Education Is Important for the Prevention of Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Yun-Mi Yong, Kyung-Mi Shin, Kang-Min Lee, Jae-Young Cho, Sun-Hye Ko, Min-Hyang Yoon, Tae-Won Kim, Jong-Hyun Jeong, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(2):154-163. Published online March 10, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.2.154
- 3,945 View
- 40 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated whether an intensive individualized reinforcement education program could influence the prevention of hypoglycemic events in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods From March 2013 to September 2013, patients aged 35 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes who had not previously participated in diabetes education, and treated with insulin or a sulfonylurea-containing regimen were included in the study. After structured group education, the patients assigned to the intensive individualized education group (IT) were requested to visit for reinforcement. All subjects in the IT were encouraged to self-manage dose adjustments. Participants in both groups (control group [CG, group education only;
n =22] and IT [n =24]) attended follow-up visits at 2, 8, 12, and 24 weeks. At each visit, all patients were asked whether they had experienced hypoglycemia.Results The total study population consisted of 20 men (43.5%; mean age and diabetic duration of 55.9±11.0 and 5.1±7.3 years, respectively). At 24 weeks, there were no significant differences in hemoglobin A1c values between the CG and IT. The total number of hypoglycemic events per patient was 5.26±6.5 in the CG and 2.58±2.3 times in the IT (
P =0.004). Adherence to lifestyle modification including frequency of exercise, self-monitoring of blood glucose, or dietary habit was not significantly different between the groups. However, adherence to hypoglycemia management, especially the dose adjustment of medication, was significantly higher in the IT compared with the CG.Conclusion Compared with the structured group education, additional IT resulted in additional benefits in terms of avoidance of hypoglycemia and treating hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness of the SUGAR intervention on hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A pragmatic randomised controlled trial
Huda Y. Almomani, Carlos Rodriguez Pascual, Paul Grassby, Keivan Ahmadi
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2023; 19(2): 322. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional study on risk factors for severe hypoglycemia among Insulin-Treated elderly type 2 diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) patients in Singapore
Michelle Shi Min Ko, Wai Kit Lee, Li Chang Ang, Su-Yen Goh, Yong Mong Bee, Ming Ming Teh
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 185: 109236. CrossRef - Management Status of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus at General Hospitals in Korea: A 5-Year Follow-Up Study
Jin Hee Jung, Jung Hwa Lee, Hyang Mi Jang, Young Na, Hee Sun Choi, Yeon Hee Lee, Yang Gyo Kang, Na Rae Kim, Jeong Rim Lee, Bok Rye Song, Kang Hee Sim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 64. CrossRef - Anti-hyperglycemic Medication Compliance: A Quality Assurance Project
Rayan Mamoon, Md Y Mamoon, Debbie Hermanstyne, Issac Sachmechi
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Randomised controlled trial of pharmacist-led patient counselling in controlling hypoglycaemic attacks in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (ROSE-ADAM): A study protocol of the SUGAR intervention
Huda Y. Almomani, Carlos Rodriguez Pascual, Sayer I. Al-Azzam, Keivan Ahmadi
Research in Social and Administrative Pharmacy.2021; 17(5): 885. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Soo-Yeon Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 263. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes patients’ views on prevention of hypoglycaemia – a mixed methods study investigating self-management issues and self-identified causes of hypoglycaemia
Stijn Crutzen, Tessa van den Born-Bondt, Petra Denig, Katja Taxis
BMC Family Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cross‐sectional analysis of emergency hypoglycaemia and outcome predictors among people with diabetes in an urban population
Chukwuma Uduku, Valentina Pendolino, Ian Godsland, Nick Oliver, Monika Reddy, Rachael T. Fothergill
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Short-term efficacy of high intensity group and individual education in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized single-center trial
R. Reale, A. Tumminia, L. Romeo, N. La Spina, R. Baratta, G. Padova, L. Tomaselli, L. Frittitta
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2019; 42(4): 403. CrossRef - The role of structured education in the management of hypoglycaemia
Ahmed Iqbal, Simon R. Heller
Diabetologia.2018; 61(4): 751. CrossRef - Association of diabetes therapy-related quality of life and physical activity levels in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving medication therapy: the Diabetes Distress and Care Registry at Tenri (DDCRT 17)
Yasuaki Hayashino, Satoru Tsujii, Hitoshi Ishii
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(2): 165. CrossRef - Insulin Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 367. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 967. CrossRef - Physician-Directed Diabetes Education without a Medication Change and Associated Patient Outcomes
Hun-Sung Kim, Hyunah Kim, Hae-Kyung Yang, Eun Young Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In Young Choi, Hyeon Woo Yim, Bong-Yun Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(3): 187. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and Health Costs
Yong-ho Lee, Gyuri Kim, Eun Seok Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(1): 11. CrossRef - Association between estimated blood glucose levels and glycated hemoglobin levels
Seon-Ah Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(3): 457. CrossRef - Characteristics of Hypoglycemia Pateints Visiting the Emergency Department of a University Hospital
Sang-Hyeon Choi, Deok-Ki Youn, Moon-Gi Choi, Ohk-Hyun Ryu
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(3): 202. CrossRef - Experiences of Diabetes Education among Educators of Diabetes : a content analysis approach
Soo Jin Kang, Soo Jung Chang
Journal of Korean Public Health Nursing.2016; 30(2): 221. CrossRef
- Effectiveness of the SUGAR intervention on hypoglycaemia in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: A pragmatic randomised controlled trial
- Statin Discontinuation after Achieving a Target Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Cardiovascular Disease: A Randomized Controlled Study
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(1):64-73. Published online February 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.64
- 3,869 View
- 48 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study investigated the rate of relapse of dyslipidemia and the factors which could predict relapse following a short-term statin discontinuation after achieving a target low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level in type 2 diabetic patients without cardiovascular disease (CVD).
Methods Ninety-nine subjects on rosuvastatin treatment and whose LDL-C level was lower than 100 mg/dL were randomly assigned to discontinue or maintain statin treatment at a 2:1 ratio. The subjects were followed-up after 10 weeks. A relapse of dyslipidemia was defined as a reascent of LDL-C level to greater than 100 mg/dL.
Results The statin discontinuation group had a significant rate of relapse compared to the maintenance group (79% vs. 3%, respectively). Pretreatment and baseline lipid levels, their ratios, and hemoglobin A1c level were significantly different between the relapse and nonrelapse groups. The pretreatment and baseline lipid profiles and their ratios were independently associated with relapse. The pretreatment LDL-C level was the most useful parameter for predicting a relapse, with a cutoff of 123 mg/dL. During the follow-up period, no CVD event was noted.
Conclusion The relapse rate of dyslipidemia was high when statins were discontinued in type 2 diabetic patients without CVD. Statin discontinuation should be considered carefully based on the pretreatment lipid profiles of patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy
Federico Rea, Annalisa Biffi, Raffaella Ronco, Matteo Franchi, Simona Cammarota, Anna Citarella, Valeria Conti, Amelia Filippelli, Carmine Sellitto, Giovanni Corrao
JAMA Network Open.2021; 4(6): e2113186. CrossRef - Visit-to-visit variability of lipid measurements and the risk of myocardial infarction and all-cause mortality: A prospective cohort study
Xiaoxue Liu, Shouling Wu, Qiaofeng Song, Xizhu Wang
Atherosclerosis.2020; 312: 110. CrossRef - 2018 Guidelines for the management of dyslipidemia
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Young Lee, Byung Jin Kim, Eun Mi Kim, YoonJu Song, Jeong Hyun Lim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Jin Oh Na, Kwang-Yeol Park, Mi Sun Oh, Sang Youb Han, Junghyun Noh, Kyung Hee Yi, Sang-Hak L
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 34(4): 723. CrossRef - 2018 Guidelines for the Management of Dyslipidemia in Korea
Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Young Lee, Byung Jin Kim, Eun Mi Kim, YoonJu Song, Jeong Hyun Lim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Jin Oh Na, Kwang-Yeol Park, Mi Sun Oh, Sang Youb Han, Junghyun Noh, Kyung Hee Yi, Sang-Hak L
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2019; 8(2): 78. CrossRef - Patterns of statin use and long‐term adherence and persistence among older adults with diabetes
Richard Ofori‐Asenso, Jenni Ilomäki, Mark Tacey, Ella Zomer, Andrea J. Curtis, J. Simon Bell, Sophia Zoungas, Danny Liew
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(9): 699. CrossRef - Effect of visit-to-visit LDL-, HDL-, and non-HDL-cholesterol variability on mortality and cardiovascular outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention
Eun Young Lee, Yeoree Yang, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Wook Sung Chung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kiyuk Chang
Atherosclerosis.2018; 279: 1. CrossRef - Change in ALT levels after administration of HMG‐CoA reductase inhibitors to subjects with pretreatment levels three times the upper normal limit in clinical practice
Hyunah Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Seo Yeon Baik, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Therapeutics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Orthodox religious fasting as a medical nutrition therapy for dyslipidemia: where do we stand and how far can we go?
Theocharis Koufakis, Spyridon N Karras, Pantelis Zebekakis, Kalliopi Kotsa
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2018; 72(4): 474. CrossRef - Phenotyping of Korean patients with better-than-expected efficacy of moderate-intensity statins using tensor factorization
Jingyun Choi, Yejin Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, In Young Choi, Hwanjo Yu, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0197518. CrossRef - Impact of educational outreach intervention on enhancing health care providers' knowledge about statin therapy prescribing in Malaysian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mohamed Hassan Elnaem, Mohamad Haniki Nik Mohamed, Hasniza Zaman Huri, Shah M Azarisman
Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice.2018; 24(3): 521. CrossRef - Use of Moderate‐Intensity Statins for Low‐Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level above 190 mg/dL at Baseline in Koreans
Hun‐Sung Kim, Hyeseon Lee, Sue Hyun Lee, Yoo Jin Jeong, Tong Min Kim, So Jung Yang, Sun Jung Baik, Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, In‐Young Choi, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Ju Han Kim
Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology.2017; 121(4): 272. CrossRef - Cholesterol variability and the risk of mortality, myocardial infarction, and stroke: a nationwide population-based study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Heart Journal.2017; 38(48): 3560. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - The differences in the incidence of diabetes mellitus and prediabetes according to the type of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors prescribed in Korean patients
Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Yoo Jin Jeong, Sun Jung Baik, So Jung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, In Young Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Pharmacoepidemiology and Drug Safety.2017; 26(10): 1156. CrossRef - Statin for the Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(1): 32. CrossRef
- Cardiovascular Outcomes and Mortality Associated With Discontinuing Statins in Older Patients Receiving Polypharmacy
- Higher Prevalence and Awareness, but Lower Control Rate of Hypertension in Patients with Diabetes than General Population: The Fifth Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2011
- Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Kyungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Bong-Yun Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(1):51-57. Published online February 19, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.1.51
- 3,829 View
- 29 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rate of hypertension in Korean adults with diabetes using nationally representative data.
Methods Using data of 5,105 adults from the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2011 (4,389 nondiabetes mellitus [non-DM]), 242 newly diagnosed with DM (new-DM), and 474 previously diagnosed with DM (known-DM), we analyzed the prevalence of hypertension (mean systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg, or use of antihypertensive medication) and control rate of hypertension (blood pressure [BP] <130/80 mm Hg).
Results The prevalence of hypertension in diabetic adults was 54.6% (44.4% in new-DM and 62.6% in known-DM,
P <0.0001 andP <0.0001, respectively) compared with non-DM adults (26.2%). Compared to non-DM, awareness (85.7%,P <0.001) and treatment (97.0%,P =0.020) rates were higher in known-DM, whereas no differences were found between new-DM and non-DM. Control rate among all hypertensive subjects was lower in new-DM (14.9%), compared to non-DM (35.1%,P <0.001) and known-DM (33.3%,P =0.004). Control rate among treated subjects was also lower in new-DM (25.2%), compared to non-DM (68.4%,P <0.0001) and known-DM (39.9%,P <0.0001).Conclusion Higher prevalence and low control rate of hypertension in adults with diabetes suggest that stringent efforts are needed to control BP in patients with diabetes, particularly in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension in Vietnam: current burden, trends over time, and correlated factors
Thi Hoang Lan Vu, Thi Tu Quyen Bui, Quoc Bao Tran, Quynh Nga Pham, Duc Truong Lai, Tu Hoang Le, Van Minh Hoang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Ja
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 1. CrossRef - Time Trends in Comorbidity and Management of Hypertension and Self-reported Diabetes: A 15-Year Nationwide Longitudinal Study in China
Yixuan Li, Xiaomin Sun, Junxiang Wei, Jing Wu, Youfa Wang
American Journal of Hypertension.2021; 34(8): 810. CrossRef - Impact of Sociodemographic Characteristics, Lifestyle, and Obesity on Coexistence of Diabetes and Hypertension: A Structural Equation Model Analysis amongst Chinese Adults
Wenwen Wu, Jie Diao, Jinru Yang, Donghan Sun, Ying Wang, Ziling Ni, Fen Yang, Xiaodong Tan, Ling Li, Li Li, Lanfranco D Elia
International Journal of Hypertension.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of a Single-Pill Combination of Olmesartan/Amlodipine/Hydrochlorothiazide in Korean Patients with Essential Hypertension (RESOLVE): A Large, Observational, Retrospective, Cohort Study
Sung-Ji Park, Si Jae Rhee
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(8): 3500. CrossRef - Comprehensive Identification of Key Genes Involved in Development of Diabetes Mellitus-Related Atherogenesis Using Weighted Gene Correlation Network Analysis
Qi Huang, Guoxiong Deng, Rongguo Wei, Qiaoye Wang, Donghua Zou, Jinru Wei
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of hypertension among different metabolic phenotypes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
Atieh Mirzababaei, Hadis Mozaffari, Sakineh Shab-Bidar, Alireza Milajerdi, Kurosh Djafarian
Journal of Human Hypertension.2019; 33(5): 365. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Evaluation of an association between long sleep duration and periodontal disease among men and women using nationally representative data
Kyungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jun-Beom Park
Gaceta Sanitaria.2018; 32(2): 143. CrossRef - Association between oral health behavior and periodontal disease among Korean adults
Kyungdo Han, Jun-Beom Park
Medicine.2017; 96(7): e6176. CrossRef - Age threshold for moderate and severe periodontitis among Korean adults without diabetes mellitus, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, and/or obesity
Kyungdo Han, Jun-Beom Park
Medicine.2017; 96(33): e7835. CrossRef - Clinical Course and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 482. CrossRef - Different effect of alcohol consumption on hypertension according to metabolic health status
H K Yang, K Han, Y-M Park, H-S Kwon, K-H Yoon, S-H Lee
Journal of Human Hypertension.2016; 30(10): 591. CrossRef - Differential Association of Metabolic Risk Factors with Open Angle Glaucoma according to Obesity in a Korean Population
Hyun-Ah Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yun-Ah Lee, Jin A Choi, Yong-Moon Park
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Jong Young Choi, Kyungdo Han, Anwar T Merchant, Yong-Moon Park
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2016; 15(1): 39. CrossRef - Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Recurrent Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Kyoungil Min, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, James M Wright
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(10): e0164807. CrossRef - Lipoprotein(a) predicts the development of diabetic retinopathy in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Jin A. Choi, Jinwoo Kwon, Donghyun Jee, Yang Kyung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2016; 10(2): 426. CrossRef - Elevated lipoprotein(a) levels predict cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a 10-year prospective cohort study
Tae-Seok Lim, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(6): 1110. CrossRef - The association of incident hypertension with metabolic health and obesity status: definition of metabolic health does not matter
Yu Mi Kang, Chang Hee Jung, Jung Eun Jang, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Eun Hee Kim, Joong‐Yeol Park, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Woo Je Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2016; 85(2): 207. CrossRef - The association between abnormal heart rate variability and new onset of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A ten-year follow-up study
Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Hyung-Wook Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 108(1): 31. CrossRef - Obesity as a Potential Risk Factor for Blepharoptosis: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008-2010
Ji-Sun Paik, Su-Kyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sang-Duck Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Suk-Woo Yang, Michele Madigan
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(7): e0131427. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis of low density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering therapy in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: single-pill regimen (amlodipine/atorvastatin) versus double-pill regimen (amlodipine+atorvastatin)
Ji-Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Lee, Su-Kyoung Ko, Bong-Soo Cha
Epidemiology and Health.2015; 37: e2015010. CrossRef - Early Renal Abnormalities as an Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes
Francesca Viazzi, Barbara Bonino, Elena Ratto, Salvatore De Cosmo, Roberto Pontremoli
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2014; 21(4): 257. CrossRef
- Comorbidities of diabetes and hypertension in Vietnam: current burden, trends over time, and correlated factors
- Erratum: Author's Name Correction. Diabetic Retinopathy and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ji-Hoon Kim, Keon-Woong Moon, Yong-Moon Park, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):488-488. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.488
- 2,690 View
- 23 Download
- 1 Crossref

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





